Functions
Possible Operators
| Operation | Description |
| + | Sum of parameters. |
| - | Subtraction of parameters. |
| * | Multiplication of parameters. |
| / | Division of parameters. |
| % | Modulus of division. |
| ^ | Degree of parameter. |
| () | Parenthesis. The operation in it has the priority in formula |
CONCAT
This function accepts any amount of values and returns the concatenated string as a value.
Structure: CONCAT(value1, value2, … ,valueN)
Where valueN is any value type.
Example: CONCAT(200, “_premium”) → “200_premium”
Business Case: Very convenient to use for setting column names for the LOOKUP or LOOKRANGE functions.
MAX
This function accepts any amount of numeric values and returns the highest possible value.
Structure: MAX(value1, value2, … ,valueN)
Where valueN is any numeric value
Example: MAX(200, premium)
Business Case: Very convenient to use for minimal premium calculation, when calculated premium should not be less than the fixed amount (e.g. 200).
MIN
This function accepts any amount of numeric values and returns the lowest possible value:
Structure: MIN(value1, value2, … ,valueN)
Where valueN is any numeric value
Example: MIN(1000, premium)
Business Case: Very convienient to use for maximum (top) premium calculation, when calculated premium should not be more than the fixed amount (eg. 1000).
SUM
This function accepts any amount of numeric values and returns mathematical sum of them.
Structure: SUM(value1, value2, … ,valueN)
Where valueN is any numeric value
Example: SUM(500, premium, extra_premium)
AVG
This function accepts any amount of numeric values and returns mathematical average of them.
Structure: AVG(value1, value2, … ,valueN)
Where valueN is any numeric value
Example: AVG(20000, car_value_1, car_value_2)
LOOKUP
This function looks for a specific column value in a datatable when other columns match to the given value.
Structure: LOOKUP(dataTable, returnColumn, value1, column1, value2, column2, …, valueN, columnN)
Where:
- dataTable - name of the lookup data table
- returnColumn - name of the column of located row, which value needs to be returned.
- columnN - data table column name, where the given value (valueN) is found in that column and matched with the returnColumn value in the same row.
Example: LOOKUP("wheels", "rate", "type", aircraft_wheel_type)
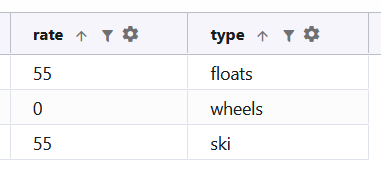
LOOKRANGE
This function looks for a specific row where given value is in the range of columns and returns the given returnColumn value.
Structure: LOOKRANGE(dataTable, returnColumn, value, columnRangeFrom, columnRangeTo)
Where:
- dataTable - name of the lookup data table
- returnColumn - name of the column of located row, which value needs to be returned.
- value - value used to check in range of columns.
- columnRangeFrom - data table column used as a lower range threshold.
- columnRangeTo - data table column used as an upper range threshold.
Example: LOOKRANGE("utilization", "loading", aircraft_utilization, "from", "to")
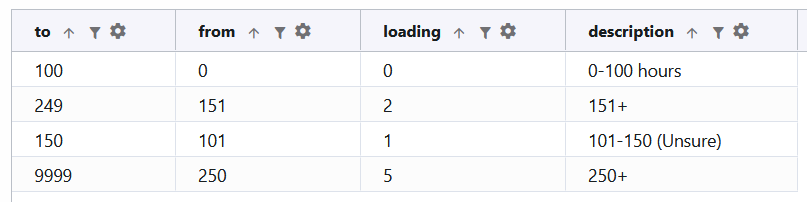
IF
This function checks given condition and returns one value if true another value if false.
Structure: IF(value, operator, checkedWith, trueValue, falseValue)
Where:
- value - provided value for checking.
- operator - checking operator, possible operators: <, >, >=, <=, ==.
- checkedWith - value used to check with given value.
- trueValue - value returned if condition is true.
- falseValue - value returned if condition is false.
Example: IF(age, “>”, “70”, “retired”, “still young”)
IFEQUALS
This checks if value equals to checkedValue and returns one value if true, another if false.
Structure: IFEQUALS(value, checkedWith, trueValue, falseValue)
Where:
- value - provided value for checking.
- checkedWith - value used to check with given value.
- trueValue - value returned if condition is true.
- falseValue - value returned if condition is false.
Example: IFEQUALS(aircraft_type, "helicopter", "rotorwing", "fixedwing")
IFNOTEQUALS
This checks if value does not equal to checkedValue and returns one value if true, another if false.
Structure: IFNOTEQUALS(value, checkedWith, trueValue, falseValue)
Where:
- value - provided value for checking.
- checkedWith - value used to check with given value.
- trueValue - value returned if condition is true.
- falseValue - value returned if condition is false.
Example: IFNOTEQUALS(aircraft_wing_type, "rotorwing", aircraft_pilot_age_loading_rw, aircraft_pilot_age_loading_fw)
IFGREATER
This checks if the value is greater to the checkedValue and returns one value if true, another if false.
Structure: IFGREATER(value, checkedWith, trueValue, falseValue)
Where:
- value - provided value for checking.
- checkedWith - value used to check with given value.
- trueValue - value returned if condition is true.
- falseValue - value returned if condition is false.
Example: IFGREATER(aircraft_passengers_seats, 3, 3, 0)
IFGREATEREQUALS
This checks if the value is greater or equals to the checkedValue and returns one value if true, another if false.
Structure: IFGREATEREQUALS(value, checkedWith, trueValue, falseValue)
Where:
- value - provided value for checking.
- checkedWith - value used to check with given value.
- trueValue - value returned if condition is true.
- falseValue - value returned if condition is false.
Example: IFGREATEREUQALS(aircraft_passengers_seats, 3, 3, 0)
IFLESS
This checks if the value is less to the checkedValue and return one value if true, another if false.
Structure: IFLESS(value, checkedWith, trueValue, falseValue)
Where:
- value - provided value for checking.
- checkedWith - value used to check with given value.
- trueValue - value returned if condition is true.
- falseValue - value returned if condition is false.
Example: IFLESS(aircraft_pilot_age, 71, 5, 0)
IFLESSEQUALS
This checks if the value is less or equals to the checkedValue and return one value if true, another if false.
Structure: IFLESS(value, checkedWith, trueValue, falseValue)
Where:
- value - provided value for checking.
- checkedWith - value used to check with given value.
- trueValue - value returned if condition is true.
- falseValue - value returned if condition is false.
Example: IFLESS(aircraft_pilot_age, 71, 5, 0)
IFNA
This checks if the value is empty or null, then returns alternative value, otherwise the provided value.
Structure: IFNA(value, alternative)
Where:
- value - provided value for checking.
- alternative - returned alternative value.
Example: IFNA(country, “UK”)
INRANGE
This function looks for the specific parameter in the given range, if true returns one value, otherwise another.
Structure: INRANGE(value, from, to, valueInRange, valueOutRange)
Where:
- value - provided value for checking.
- from - lower range threshold.
- to - upper range threshold.
- valueInRange - value to be returned if the provided value is in the range
- valueOutRange - value to be returned if the provided value is out of the range
Example: INRANGE(year_of_birth, 1946, 1964, “boomer”,”other”)
CASE
This function accepts given value and multiple cases combination (case ,value), if the given value matches case, then returns case’s value.
Structure: CASE(value, case1, value1, … ,caseN, valueN)
Where:
- value - provided value for checking.
- caseN - matching case for the value.
- valueN - any numeric value to be returned if matches case.
Example: CASE(monthly_benefit, 1500, "too much", 1000, “enough”)
LOWER
This function transforms string value to the lowercase. If numeric value is given, it will be returned as unchanged.
Structure: LOWER(value)
Where:
- value - provided value for transformation.
Example: LOWER(country)
UPPER
This function transforms string value to the uppercase. If numeric value is given, it will be returned as unchanged.
Structure: UPPER(value)
Where:
- value - provided value for transformation.
Example: UPPER(country)
FOREACH
This function process all the given array through calculation steps which belongs to the same name.
Structure: FOREACH(name, array, key)
Where:
- name - name of the cycle.
- array - array of parameters passed to cycle.
- key - key prefix for array parameters.
Example: FOREACH(“aircraft_cycle”, aircrafts, “aircraft”)
NUMBER
This function converts the given value to the number type value. If fails to convert then returns 0.
Structure: NUMBER(value)
Where:
- value - provided value for transformation.
Example: NUMBER(age)
DECIMAL
This function converts the given value to the decimal type value. If fails to convert then returns 0.
Structure: DECIMAL(value)
Where:
- value - provided value for transformation.
Example: DECIMAL(age)
STRING
This function converts the given value to the string type value.
Structure: STRING(value)
Where:
- value - provided value for transformation.
Example: STRING(price)
HALT
This function stops all the following steps processing in the calculator. Returns rule provided as a parameter.
Structure: HALT(rule)
Where:
- rule - returns rule as output by given rule code.
Example: HALT(“DEC-001“)
SUMMARRAY
This function process the given array and sums provided element(by key) values. Returns a numeric field.
Structure: SUMARRAY(array, key)
Where:
- array - array of parameters passed to function.
- key - keys of elements used in summing. Must be numerical values.
Example: SUMARRAY(aircrafts, “price”)
COUNTARRAY
This function process the given array and counts records.
Structure: COUNTARRAY(array)
Where:
- array - array of parameters passed to function.
Example: COUNTARRAY(aircrafts)